Introduction
This post talks about a simple Convolution Neural Network (CNN) which is used to
recognize characters i.e. Numeric and Alphabet. We have total 10 Numeric and 26
Alphabets that sums up the total number of classes in our network to 36. In
order to get characters from the License Plates we first need to use some kind
of License Plate detector which is followed by a Character segmentation method
in order to extract character from the License Plates (LP).
Architecture of model
We have used very familiar CNN network for OCR, usually CNN consists of some
Convolution layers(All Convolution layers are followed by max pooling layers)
and fully connected layers.
We already know much about Convolution layers so i am gonna talk about max
pooling and fully connected layers here.
Pooling layers section would reduce the number of parameters when the
images are too large. Spatial pooling also called sub-sampling or down-sampling
which reduces the dimensionality of each map but retains important information.
Spatial pooling can be of different types:
- Max Pooling
- Average Pooling
- Sum Pooling
Max pooling takes the largest element from the rectified feature map. Taking the
largest element could also take the average pooling. Sum of all elements in the
feature map call as sum pooling.
The layer we call as Fully Connected Layer (FC) layer, we flattened our
matrix into vector and feed it into a fully connected layer like a neural
network. After the last max pooling layer there will be a sequence of FC layers.
Finally we will apply an activation function such as softmax or sigmoid to
classify the outputs between classes.
Model configuration is given below:
Total layer : 14
- Convolution with 64 different filters in size of (3x3)
- Max Pooling by 2
- ReLU activation function
- Batch Normalization
- Convolution with 128 different filters in size of (3x3)
- Max Pooling by 2
- ReLU activation function
- Batch Normalization
- Convolution with 256 different filters in size of (5x5)
- Max Pooling by 2
- ReLU activation function
- Batch Normalization
- Convolution with 512 different filters in size of (5x5)
- Max Pooling by 2
- ReLU activation function
- Batch Normalization
- Flattening the 3-D output of the last convolving operations.
- Fully Connected Layer with 128 units
- Fully Connected Layer with 256 units
- Fully Connected Layer with 512 units
- Fully Connected Layer with 1024 units
- Fully Connected Layer with 36 units (number of classes)
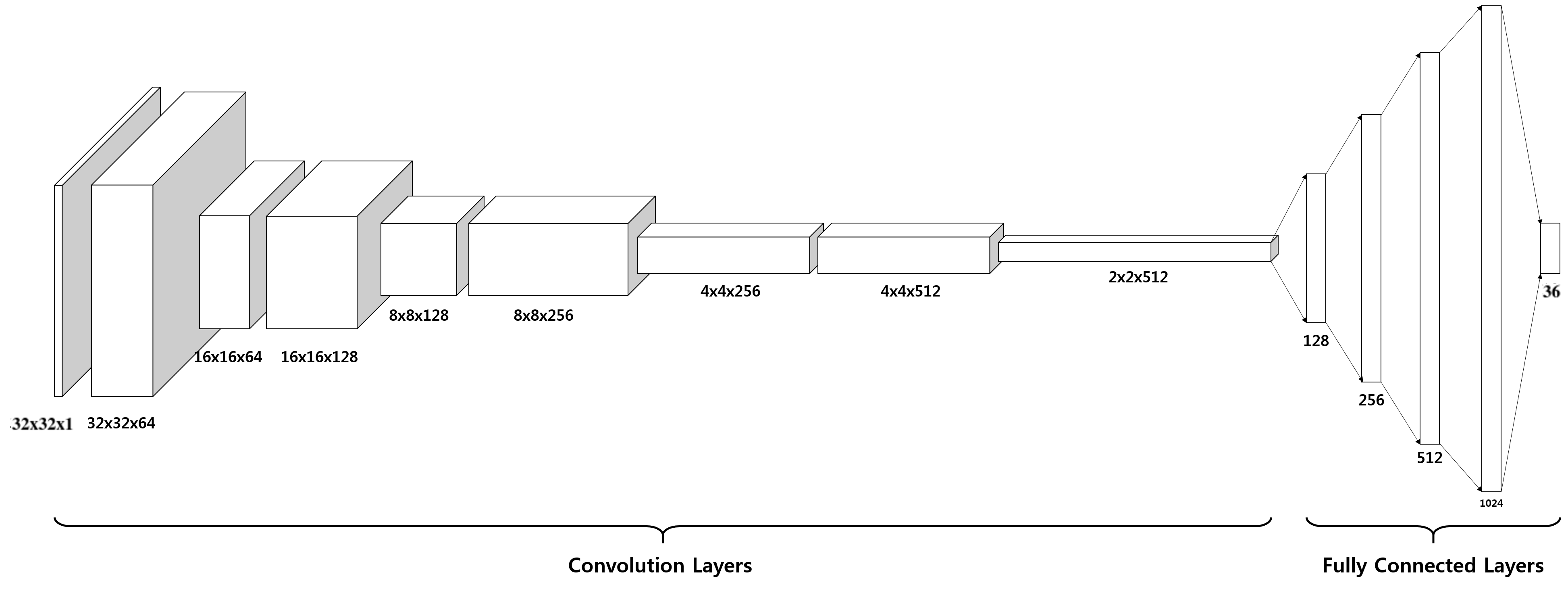
Figure 1. Architecture of model
Placeholders
Defining a placeholder in tensorflow is very common. When we want to declare our
input and output without initialization this method comes very useful. You can
use them during training of model by feeding them with training data and labels.
1 | def create_placeholders(n_H0, n_W0, n_C0, n_y): |
Once you have defined your model architecture you now need to define cost and
optimizer for your model which is defined in the next section.
Cost function and optimizer
Cost function gives degree of error between predicted and expected values and
after that it represent it in form of a real number. Whereas optimizer update
the weight parameters to minimize the cost function.
Finally, you’ll define cost, optimizer, and accuracy. The tf.reduce_mean
takes an input tensor to reduce, and the input tensor is the results of certain
loss functions between predicted results and ground truths. We have to measure
loss over 36 classes, tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logis function is
used.
When training the network, what you want is minimize the cost by applying a
algorithm of your choice. It could be SGD,AdamOptimizer,AdagradOptimizer or
something else. You have to study how each algorithm works to choose what
to use, but AdamOptimizer works fine for most cases in general.
Please find cost and optimizer sample below:
1 | learning_rate = 0.001 |
Conclusion
So in this post i have explained basic steps to train simple CNN network for any
classification task i.e. OCR in this particular post. I have given all the steps
except the training part for that you just need to use session of tensorflow
while feeding image data and labels for those images to placeholder you have
created to the session.run function.
