Circling around the parking is one of the most annoying experiences mainly because it is time consuming and quite irritating too.
However , there has been a major boost in the field of Deep Learning and Computer Vision in the past few years which enables us to create a robust and a real-time solution.

Plan Of Attack
A pipeline for the same has been created which consists of the following 5 steps :
- Finding suitable Images
- Parking zones detection
- Vehicle detection
- Plotting the vehicles as point objects on 2d-map
- Detecting whether a parking lot is vacant or occupied
Each of the 5 steps have been described in detail in the following sections :
1) Finding Suitable Images
The first step to solve any problem in Deep Learning and Computer Vision is to collect data.
In our approach , we just required 2 images throughout the entire process.
The 2 images required are:
* Image of actual camera view of the parking zones
* Image of the top-view / 2d-map of the same areaWe obtained these 2 images in the following manner :
* There are a lot of open CCTV IP cameras available freely on the internet. By using one of the websites , we were
able to get our first image which is a camera view of parking zones.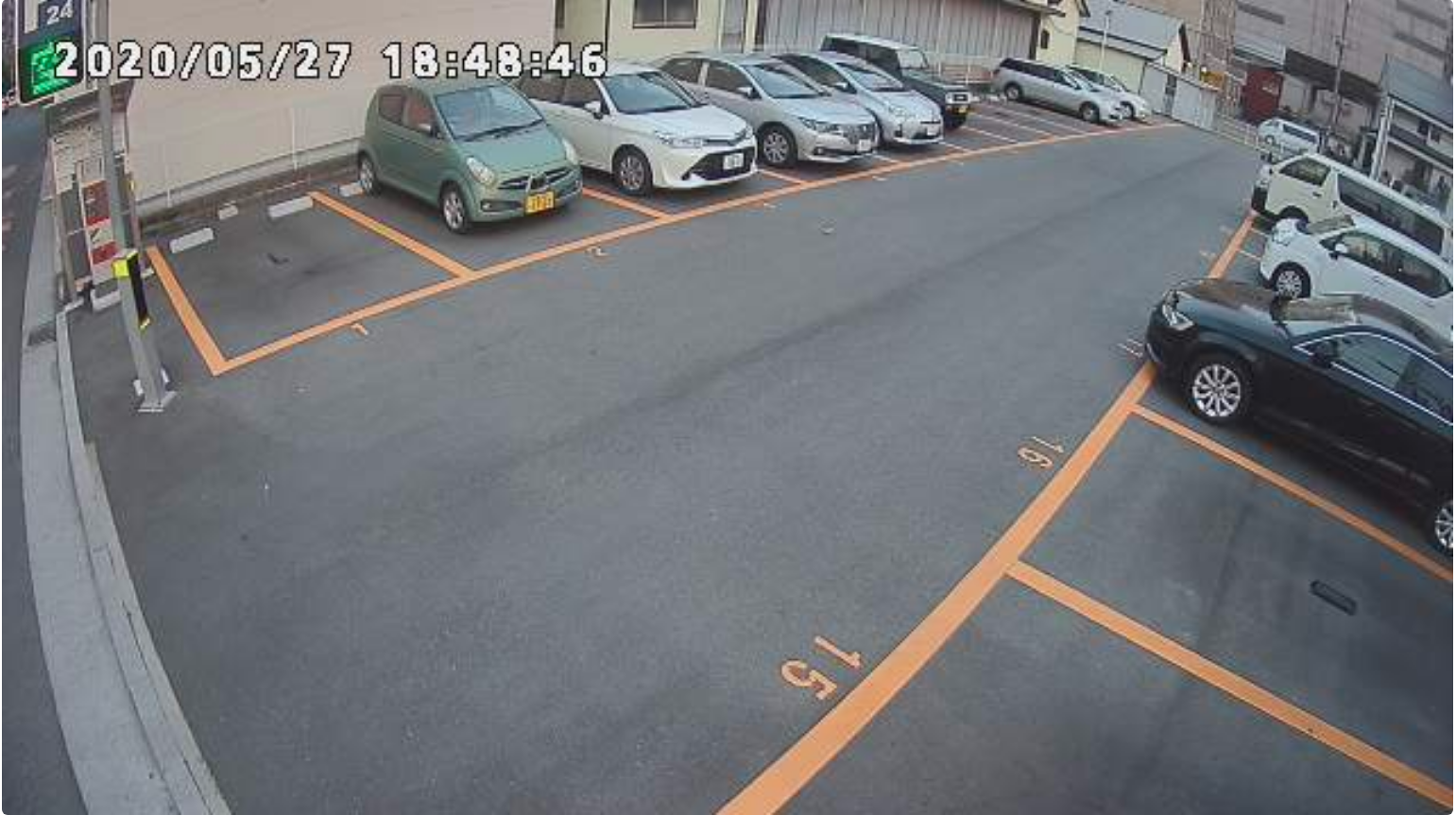
* The same website also provided us the longitude and latitude of the area which was then entered in Google Maps
in order to get it’s top-view.

We now have both the images and we are ready to proceed to the next step.
2) Parking Zones Detection
This is one of the most important tasks in the entire pipeline as almost all the remaining tasks are dependent on this. Getting these inaccurate could impact our entire pipeline leading us to an incorrect outcome.
Before jumping onto this , I had done some research and found that the following 3 methods are most commonly used to tackle this kind of problem :
* Canny edge detection and hough line transform combined with image processing could detect the lines in the parking
zones.
* Manually drawing out the contours on the parking zones.
* Directly perform vehicle detection and locate the stationary cars assuming that they are on the parking zones.Third method is based on assumptions and also not suitable for many scenarios , due to which we discarded it as an option.
We used the first method wherein we detected the lines using canny edge detection and hough line transform combined with image processing.
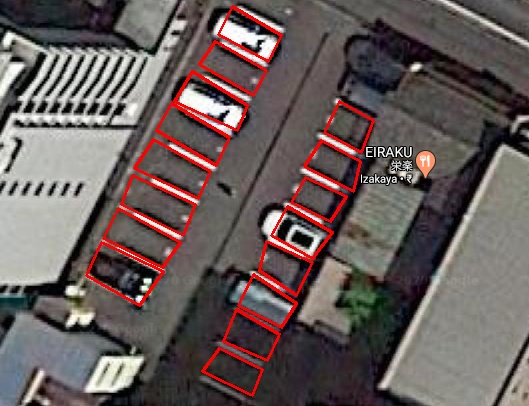

3) Vehicle Detection
In order to achieve this , we had used the state-of-the-art YOLOv3 Deep Learning object detection model.

This is a crucial step as once we get the bounding boxes accurately, only then would we be able to detect whether a parking zone is vacant or occupied.
4) Representing the vehicles as point objects on 2d-map
For this step , we would be using a very classical Computer Vision concept.
This step can be broken to the following sub-steps :
*Using Google API , we came to know the dimensions of the parking areas in both the images.
*This helped us in restricting the images to particular areas which further aided us in automatically detecting key
points in both images.
*Distortion also plays a significant role in getting accurate key-points. So had there been some information about the
planted camera , we could have undistorted the images and got more accurate key-points 
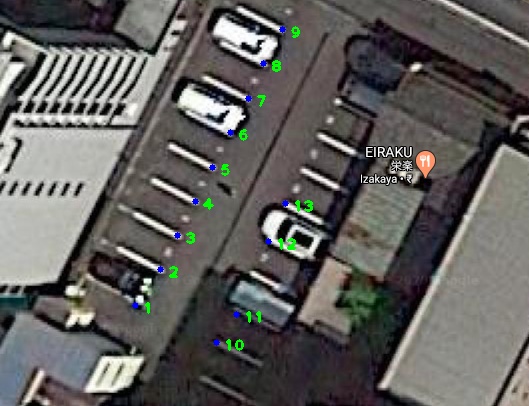

Using the key-points in the above 2 images , we calculate their homography.
We can represent vehicles as point objects by the following steps :
First step is to determine the 2d-point matrix by multiplying homography and the center coordinates of the bounding boxes
The final step in finding the 2d coordinates is to divide the 2d-point matrix obtained by third element.
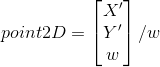
Therefore the 2d coordinates for all the vehicles are derived in similar fashion and are plotted on the 2d-map
image.
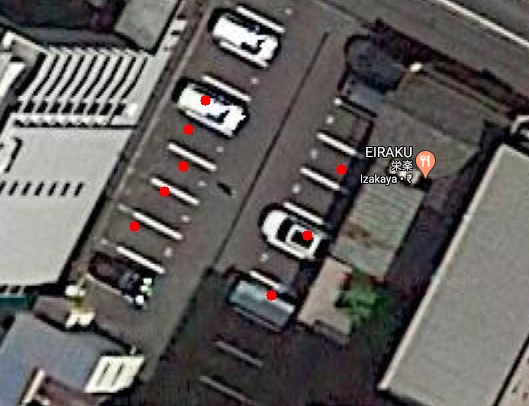

Getting these points plotted at accurate locations implies that results and calculations we got from both step 3
and step 4 are perfect.
5) Detecting whether a parking lot is vacant or occupied
Point Polygon test is used here to find whether the point is inside or outside the parking zone.
Point polygon test checks whether a point is inside the polygon or not.
It returns a negative value if the point is outside the polygon , 0 if the point is on the polygon and a
positive value if the point is inside the polygon.
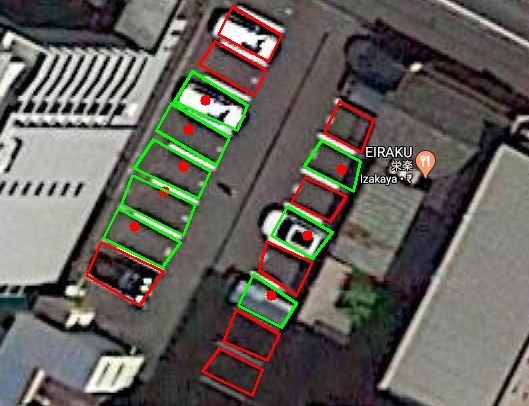
Hence as it can be seen from the image above, with the help of Deep Learning and Computer Vision , we have successfully solved this problem by following a very simple and systematic approach.
For more such exciting Deep Learning blog posts,click here.
Also, click here to know how we are leveraging AI for traffic monitoring and road safety.
